During this time of emerging “born-in-tech” insurance providers that are fast to react to changes in the market and in customer behavior, increasing pressure to speed up cycle times, reduce expenses and improve customer experiences becomes the new normal for traditional insurers.
Unfortunately, overflow of routine back-office operations, heavy reliance on manual work, and outdated methods and legacy systems make achieving these goals difficult.
Adoption of intelligent process automation in the insurance industry is believed by many to be the solution to these challenges, and it is already transforming the industry.
Contents:
How automation will transform insurance
The Hyper Automation market has been growing at breakneck speed and, according to Gartner, is expected to reach nearly US $600 billion in 2022. While the banking and financial services domain embraced this trend long ago, the adoption of automation in the insurance industry has been much slower. Insurance companies are only starting to launch pilot automation programs, with both RPA (robotic process automation) and Intelligent Automation, and the impact of these technologies on the sector is expected to be enormous. How will automation affect insurance? Here are a few expected outcomes:
- Impact on employment in insurance. Automation will eliminate many jobs, while also creating new ones. Employees freed from tedious copy-paste and data-entry tasks will be able to deliver more personalized and higher-quality customer service.
- Technological transformation. Automation tools will be built into existing IT infrastructure to ensure better integration between various systems.
- Improved and more personalized customer experience. For example, customer onboarding will change as bots can perform time-consuming activities such as anti-money laundering. This technology can help bridge the gap between employees and customers and allow more personalized service.
Hyper Automation or Intelligent Automation in insurance has the potential to help companies transform their business, become more profitable, and better adjust to market changes. However, that can only be achieved when the most valuable automation use cases are selected.
Best use cases for automation in the insurance industry
One of the critical factors for the success of automation in the insurance industry (and any other industry, for that matter) is selecting the correct use cases. There are several common insurance use cases where the implementation of intelligent automation can provide tangible results quickly and offer room to scale in the future. Let’s review some of these use cases and intelligent solutions available.
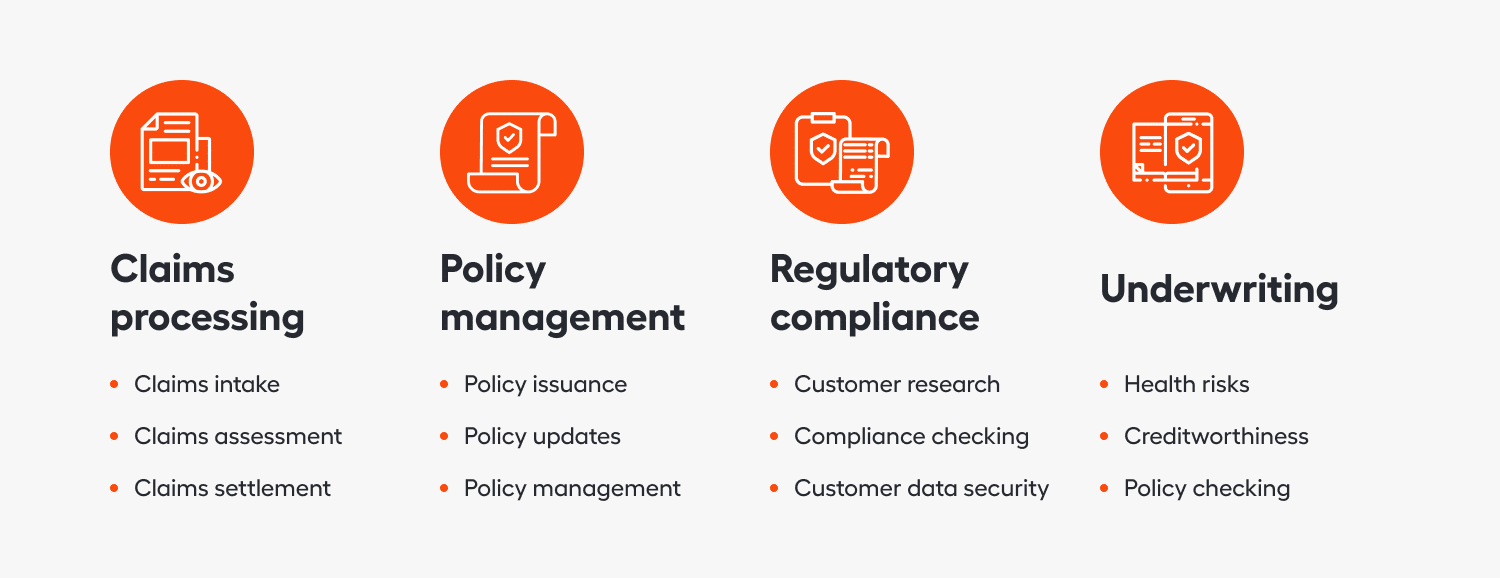
1. Claims processing
Fast and efficient claims processing is paramount to success for insurance companies — yet it’s often a time-consuming, highly manual process that’s frustrating for both insurers and customers. Typically, claim processing takes several days as insurance agents have to gather and check data from multiple sources, such as:
- medical certificates and reports for life/health insurance claims (e.g., Short Term Disability Claims Preparation)
- photos of damaged baggage and boarding passes for travel loss claims
- police reports, driver’s licenses, and vehicle damage photographs for preparing auto claims (e.g., Repair Quote Approval)
It may take even more time due to human errors, like mismatched financial data or customer details. Such delays may result in the loss of customers and other financial and reputational damage to the company.
Implementing an automated claims processing workflow, including claims intake, assessment, and finally, claims settlement, eliminates friction and cost by combining RPA, machine learning, and human expertise to streamline and speed up claims-related operations.
For example, when processing a First Notice of Loss request, an RPA bot would extract the information from the request and enter it into the claims system. If the claim is complete, a cognitive bot would validate its information and mark it approved for payment. If there is missing data, the task is routed to an agent to perform, and the bot observes how the agent handles this exception and “learns.” When the agent returns the claim to the workflow, a bot automatically sends the verified request for payment.
In another common insurance process, Paper Claims Intake, bots automatically receive paper claims once scanned, classify documents into types, extract key data points, and push the extracted data into the core claims systems — tedious, low-value, manual tasks that qualified employees spend hours on every day.
Automated claims processing reduces the amount of manual work by 80% and improves accuracy significantly, cutting down the time necessary for the process by 50% — which allows companies to process twice as many claims with the same personnel. As a result, customer experience is improved as the back office functions are performed fast and with fewer errors, delays, and annoying back-and-forth communication with customers.
2. Policy management
One more common insurance use case for Intelligent Automation is the whole cycle of policy management operations, including policy issuance and updates.
At the stage of policy issuance, pre-underwriting checks have been done, and the underwriting decision has already been made. The policy has to be issued, and information needs to be updated in internal systems and communicated to the customer. All these processes involve a lot of manual work. Pre-built RPA and AI use cases can be used to automate insurance policy issuance, thus significantly reducing the amount of time and manual work required for it.
Existing policy-holders can submit various update requests, such as address change or update of bank mandate. Insurance automation solutions for policy updates use machine learning to extract inbound changes from voice transcripts, emails, faxes, or other sources and make all required changes in the documents and internal systems.
For example, in our solution for Endorsement Request Intake and Routing, after receiving inbound requests from emails and separating email content from key attachments, ML bots identify the nature of the change request, classify supporting documents into types, and extract key data points from all relevant documents. The bots turn this information into structured data that can then be used to perform required updates and edits in the policy systems.
A broader application of automation in insurance policy management can help transform other document-intensive operations, including the processing of loss run reports, analysis of the statement of value reports, communicating explanations of evidence of insurability to customers, and other processes.
3. Regulatory compliance
Insurance companies have to comply with a significant number of regulations. Amendments to these regulations often force insurers to reorganize their business processes to adapt. Compliance breaches result in financial and operational damages to companies.
One of many compliance-centered use cases is Name Screening Alert Review for Sanctions and PEP (politically exposed persons). Screening systems generate thousands of alerts daily, and most of them are false positives. Automating their review drastically lowers the number of false positives a person must manually handle — reducing time and effort while increasing accuracy and auditability.
Other examples of time-consuming manual work that AI-driven RPA can automate include compliance checks, client research and validation of customer data, customer data security operations, and generation of regulatory reports and notifications.
4. Underwriting
Automated underwriting is another imminent transformation in the insurance industry, boosting accuracy and speed in this key operation. Underwriting involves gathering and analyzing information from multiple sources to determine and mitigate the risks associated with the chosen policy, for example:
- Health risks. Mortality charges, and hence, premiums, will go up in cases where an applicant is a smoker, especially when weighed against their current age.
- Financial limits. If the net worth of the applicant today is $X, their insurance coverage (death benefit) cannot exceed, say, $10X.
- Creditworthiness. What is the credit rating of the applicant, as per external agencies such as Experian or TransUnion CIBIL Limited?
- Duplicate policies. Does the applicant already have a policy in their name?
The whole process can take weeks. Implementation of intelligent solutions to automate insurance underwriting will significantly speed up such functions as data collection, internal systems updates, loss runs assessment, customer claims history review, and more. For example, you can automate more than 70% of the manual work involved in the New Submissions Intake process, as bots retrieve underwriting documents from emails, classify and extract the required information, cross-reference external data enrichment sources for additional data, and validate the application for completeness via custom business rules. As a result, the turnaround times for new submissions can be four times quicker.
In another use case, Medical Benefit Plan Entry and Processing, Intelligent Automation solutions reduce 80% of manual effort, including errors generated in the process.
All in all, automation solutions that combine RPA, machine learning, and human-in-the-loop to “support” AI can reduce the number of errors in underwriting operations down to almost 0%. Read more about the impact of Intelligent Automation on underwriting in our white paper, “Aim for Success with Intelligent Automation.”
Benefits of intelligent process automation in insurance
When compared to automation solutions using only the power of RPA, applying Intelligent Automation and AI in insurance operations helps achieve a faster ROI and see benefits that are unattainable with pure RPA.
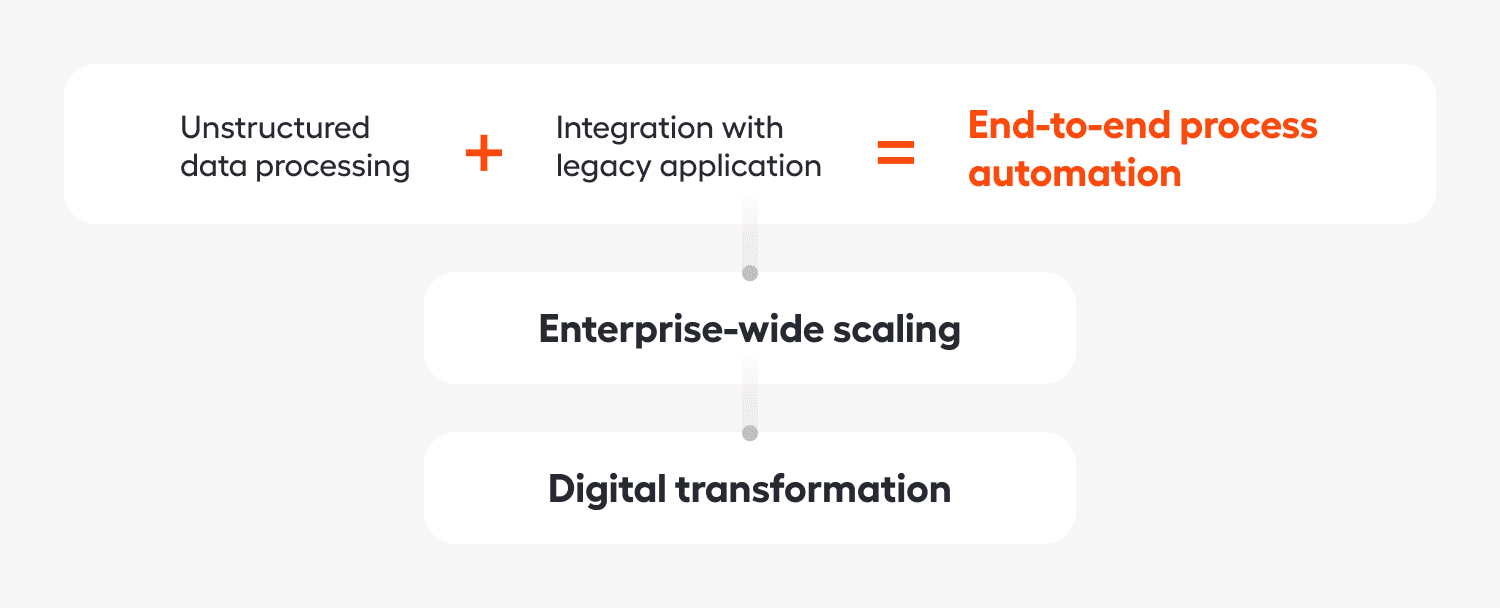
1. Unstructured data processing
Every day, insurers have to deal with massive volumes of data in various paper and electronic formats. To process a claim, an agent must gather data from multiple sources and enter it into a database. The process is manual and time-consuming. Repetition of the same routine tasks over and over again hinders human concentration, resulting in errors and creating serious inconsistencies in company records. Robots, on the other hand, excel in this aspect.
AI combined with robotic process automation can process a wider variety of documents more precisely, and can automate insurance processes end-to-end:
- download, classify, compile data from external sources
- read, sort, analyze and route emails
- extract and analyze similar data from different sources (email attachments, transcripts, scanned agreements, etc.)
2. Integration with legacy applications
Insurance companies still rely heavily on legacy apps and various programs and systems for managing business operations. Implementation of new software, such as BPM or ERP systems, often requires replacement of the existing hardware and employee retraining — which are significant investments of time and money. Due to these difficulties, many insurance companies are forced to stick to the old systems, although they no longer provide the support required for company development.
Automating operations in legacy applications are great RPA use cases in insurance. RPA bots can use existing user interfaces, which means there is minimal or no need to change current legacy systems. RPA bots can imitate human clicks and keystrokes, which makes them easy to implement in addition to the existing software and hardware. RPA bots create links between legacy and new systems without coding. They switch between various systems and applications and conduct claims processing, underwriting, customer service, onboarding, and other operations — all at the same time.
Remember that utilizing solely RPA for automation will not have tangible results, as it only will allow you to automate separate tasks included in the process. On the other hand, using intelligent insurance automation solutions that combine RPA with powerful AI capabilities will allow automation of the process end-to-end. The cognitive part of the work will be automated, and also exception-handling capabilities will be provided through a human-in-the-loop approach.
3. Additional benefits and scaling opportunities
Successful implementation of an intelligent automation program can be incredibly beneficial for an insurance company, potentially allowing an enterprise to:
- bring down the cost of automated job functions by 30–40%, while doubling their efficiency
- achieve up to 80–90% accuracy improvement
- save thousands of work hours annually
- speed services delivery by up to 80%
- free up to 30% capacity at the enterprise level
- increase overall business productivity and profitability by up to 50%
- reach up to 100% regulatory compliance
Regarding costs, a 100% return on investment can reasonably be expected within the first year of implementation, and that’s likely to multiply in the years to follow.
One of the most significant benefits that Intelligent Automation can bring is creating a framework for enterprise-wide scaling of automation and digital transformation. Building a scalable automation program may seem easy in theory: You just need to add more bots over time. But this is challenging to achieve in practice. Most processes in insurance are unstructured, high-volume, and are ultimately too complicated for traditional RPA. Introducing intelligent bots provides a solution to these automation challenges, allowing you to not only scale the number of bots deployed, but also the quality and complexity of the work they perform. Learn more in our free white paper, “Beyond Limits: Scaling Intelligent Automation.”
Overall, the potential for automation in the insurance industry is limitless. Across different geographies and sometimes even within the same company, various processes are in various stages of digitization and many can be at least partially automated. Automation is the lever that can help transform your operations, radically elevate your employee satisfaction, and improve your customer journey.
But where to start an automation program? What are the areas most suited for end-to-end process automation in insurance?
To help you find these areas, we have launched a new discovery tool: Use Case Navigator. Find real-life use cases in insurance and other industries, collected for your information and inspiration, and to help you get started with Intelligent Automation fast.
Note: The article was originally published in February 2020 and updated in October 2021 with new automation use cases.